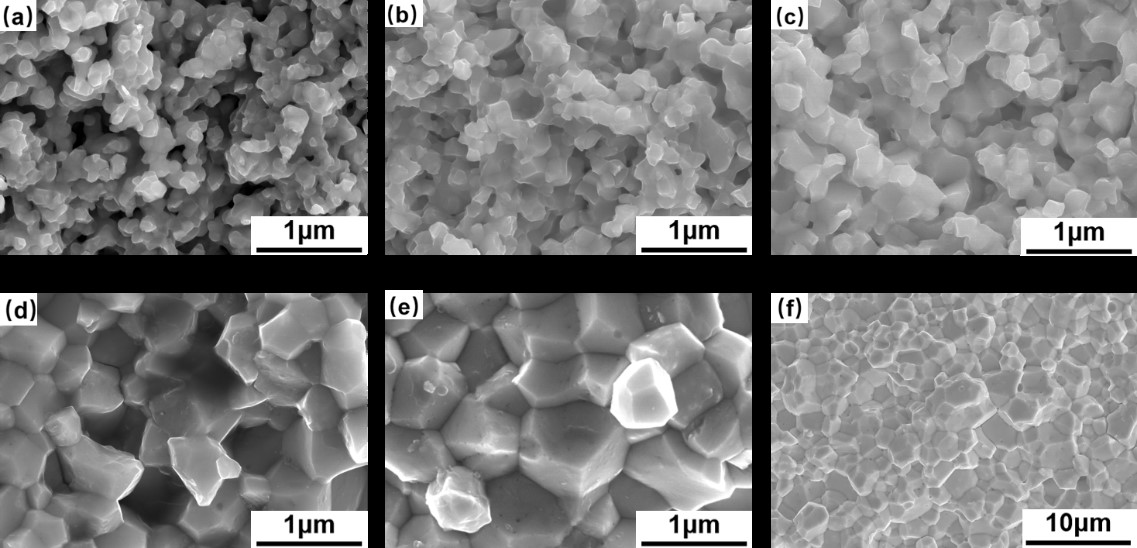
First, the solution combustion method and pure hydrogen reduction method are used to prepare Mo nanopowder. The powder is compressed under uniaxial force. The sintering experiment was carried out in a high-purity hydrogen atmosphere, and two different heating schemes were used: (i) Constant heating rate sintering, that is, the green body is heated to the preset temperature at a rate of 5 ℃/min without holding the temperature. (1000-1400°C), then cool to room temperature at a rate of 10°C/min. These experiments are used to study the sintering kinetics and to find suitable first-step sintering conditions to optimize the two-step sintering; (ii) Two-step sintering, heating the green body to T1, then cooling to T2 and holding it for a long time. The density of the sintered sample was measured by the Archimedes method. The fracture of the sample was observed under the FEI Quanta FEG 450 field emission scanning electron microscope. A field emission gun scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM, JIB 4600F) equipped with electron backscatter diffraction (EBSD, AZtec system, Oxford Instruments) was used to perform EBSD characterization of the microstructure.