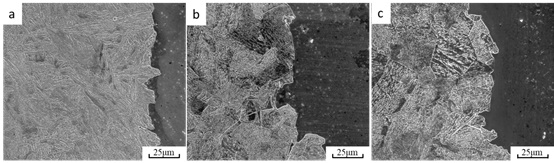
名称 : DZ2(连铸)不同部位上的冲击断口剖面图
英文名称 : Impact fracture profiles on different parts of DZ2(continuous casting)
材料 : 877
委托单位 : 钢铁研究总院
实验单位 : 钢铁研究总院中心实验室
实验方法 : 扫描电镜观测
实验设备 : FEI Quanta650热场发射扫描电子显微镜
实验条件 : 室温
说明 :
图为DZ2(连铸)钢不同部位冲击试样断口剖面图,由图可知,边部试样裂纹在扩展过程中沿着马氏体发生了多次转折,而在1/2半径和心部裂纹沿原始奥氏体界面或贝氏体以直线扩展,很少发生转折。这是由于发生马氏体相变时,马氏体通常是与奥氏体保持K-S取向关系,使得钢中具有由不同结构单元组成的分级亚结构,如原始奥氏体晶粒、板条束(packet)、板条块(block)、和亚板条块(sub-block)。这些亚结构之间的界面能够有效地阻碍裂纹的扩展,导致裂纹在马氏体中扩展时发生偏转。
英文说明 : The fracture sections of impact samples in different parts of DZ2 (continuous casting) steel are shown in the figure. It can be seen from the figure that the cracks in the edge samples take several turns along the martensite in the process of propagation, while the cracks in the 1/2 radius and center extend in a straight line along the original austenite interface or bainite, with few turns. This is because martensite usually maintains k-S orientation relationship with austenite during martensitic transformation, resulting in hierarchical substructures composed of different structural units in steel, such as primitive austenite grains, packet, block and sub-block. The interface between these substructures can effectively inhibit the crack propagation, resulting in deflection of the crack as it expands in martensite.
数据来源 : 检测数据
重点项目名称 : 苛刻环境下铁路车辆关键部件用钢-高速车轴钢基础研究数据集