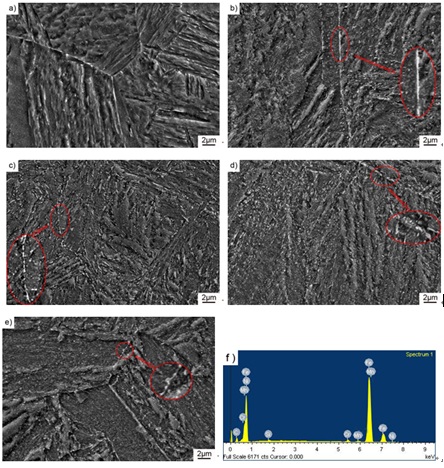
Figure (a) shows the microstructure morphology of DZ2 (0.05V0Nb) steel under scanning electron microscope (SEM) after quenching at 900℃. Figures (b), (c), (d) and (e) show the microstructure morphology of DZ2 (0.05V0Nb) steel after quenching at 900℃ and tempering at 600℃, 625℃, 650℃ and 675℃ for 1h under scanning electron microscope (SEM), and Figure (f) shows the energy spectrum. The figure shows that DZ2 (0.05 V0Nb) steel after quenching microstructure of quenched martensite lath, three kinds of steel after different temperature tempering the microstructure of tempered martensite lath, and increase with increasing tempering temperature, the part of the martensite lath dissolved, tempering temperature to 675 ℃, can see the martensite lath clear reply. At the same time, a large number of second phase particles precipitate during high temperature tempering. Energy spectrum Figure (F) shows that these dispersed precipitates are alloy carbides. When the tempering temperature rises from 600℃ to 650℃, the precipitate amount of alloy carbides increases significantly, which may be because martensite is decomposed during tempering. The supersaturated C atoms and alloying elements are dissolved from martensite to form carbides. With the increase of tempering temperature, the diffusion rate of solute atoms is accelerated, thus the carbides are precipitated. The red circle pointed by the arrow in Figure (b) ~ (e) is a partial enlarged figure, from which it can be seen more clearly that with the increase of tempering temperature, the morphology of alloy carbide changes from sheet to short rod, and finally occurs spheroidization at 675℃.