名称 : FORWARD-COPERNIC燃料棒内压
英文名称 : FORWARD-COPERNIC fuel rod internal pressure
材料 : 431
委托单位 : 中国核动力研究设计院
实验单位 : 中国核动力研究设计院
实验方法 : 数值仿真分析
实验设备 : 无
实验条件 : 无
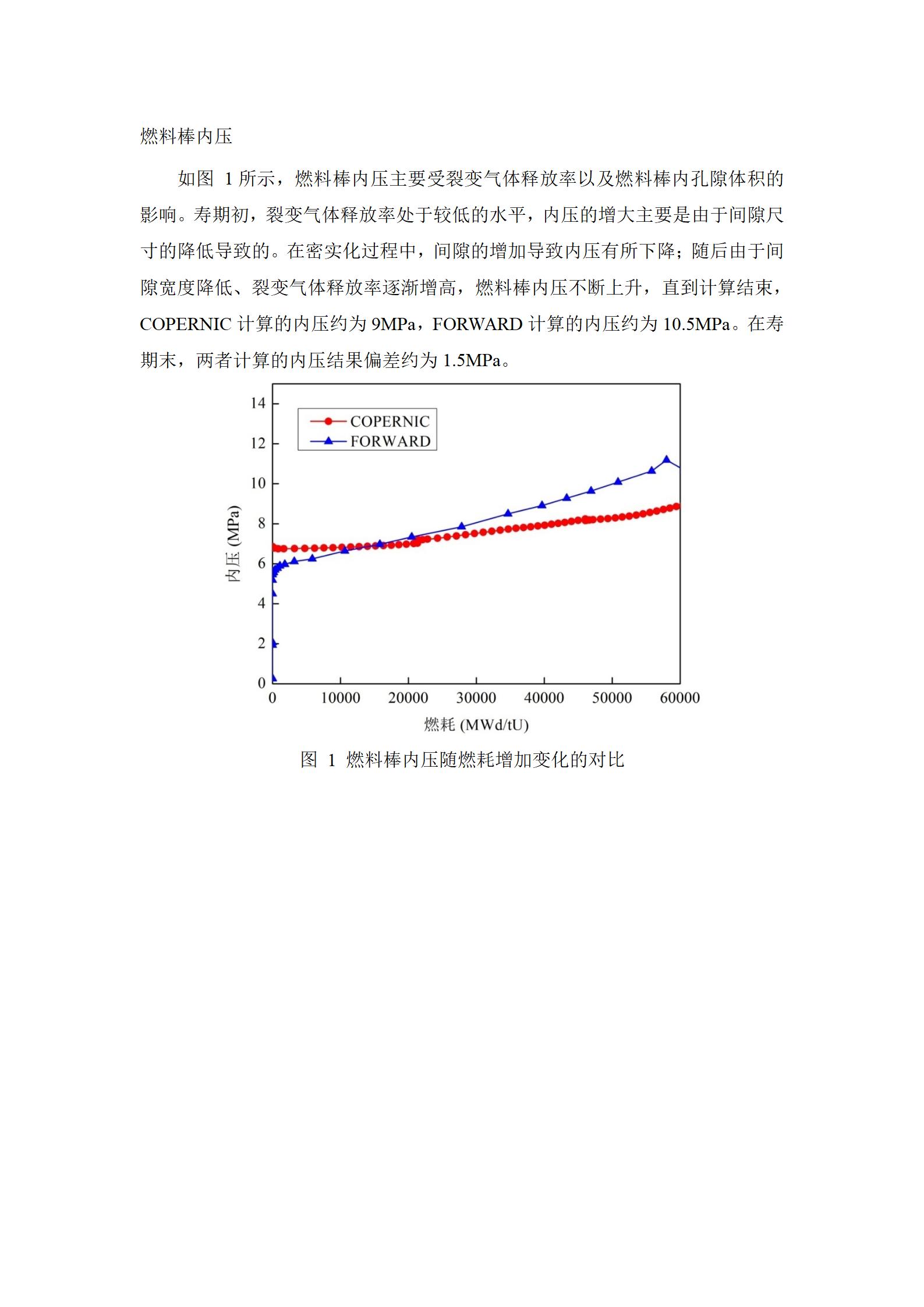
说明 : 如图 1所示,燃料棒内压主要受裂变气体释放率以及燃料棒内孔隙体积的影响。寿期初,裂变气体释放率处于较低的水平,内压的增大主要是由于间隙尺寸的降低导致的。在密实化过程中,间隙的增加导致内压有所下降;随后由于间隙宽度降低、裂变气体释放率逐渐增高,燃料棒内压不断上升,直到计算结束,COPERNIC计算的内压约为9MPa,FORWARD计算的内压约为10.5MPa。在寿期末,两者计算的内压结果偏差约为1.5MPa。
英文说明 : As shown in Figure 1, the internal pressure of the fuel rod is mainly affected by the release rate of fission gas and the pore volume in the fuel rod. At the beginning of life, the release rate of fission gas is at a low level, and the increase of internal pressure is mainly due to the reduction of gap size. In the process of densification, the increase of gap leads to the decrease of internal pressure; Subsequently, as the gap width decreases and the fission gas release rate gradually increases, the internal pressure of the fuel rod keeps rising until the end of the calculation. The internal pressure calculated by COPERNIC is about 9MPa, and the internal pressure calculated by FORWARD is about 10.5MPa. At the end of the service life, the deviation of the calculated internal pressure between the two is about 1.5MPa.
数据来源 : 数值模拟
重点项目名称 : 先进核燃料元件设计研究及材料研制
项目所属数据集 : 高安全性燃料元件设计及验证数据集