名称 : 低温高速火焰喷涂流体域网格模型
英文名称 : Fluid domain mesh model
材料 : 431
委托单位 : 中国人民解放军军事科学院国防科技创新研究院
实验单位 : 中国人民解放军军事科学院国防科技创新研究院
实验方法 : 无
实验设备 : 无
实验条件 : 无
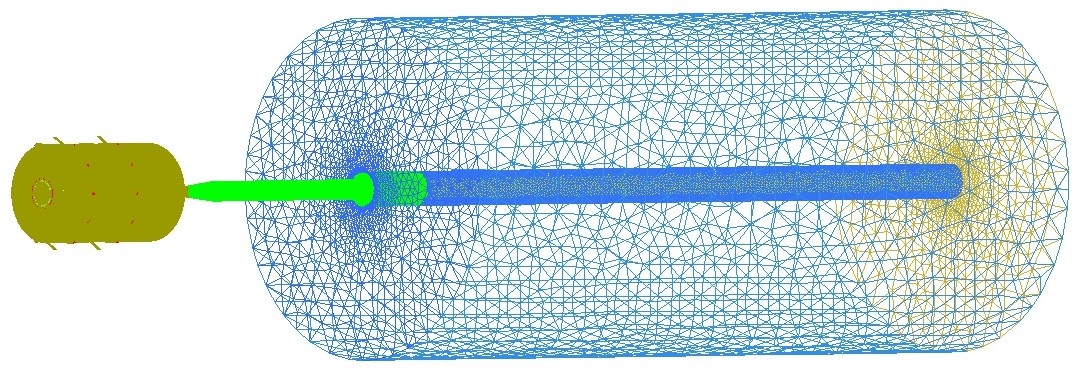
说明 : 低温高速火焰喷涂的流体域模型可分为三个部分:燃烧室流体域、喷管流体域、外部空气流体域,如图所示。在燃烧室流体域中,煤油、氧气和一次氮气从双气流雾化喷嘴射入燃烧室内部,二次氮气通过燃烧室周围的两圈圆形小孔切向注入燃烧室内部;在喷管流体域中,将不同尺寸、形状的粒子从喷管两侧注入,通过调整粒子载气的压力控制粒子的注入速度;在外部空气流体域中,设置为成分、比例与空气相同的的静态流域,最大程度还原喷口外部的自由射流区。
英文说明 : The fluid domain model of low-temperature high-speed flame spraying can be divided into three parts: the combustion chamber fluid domain, the nozzle fluid domain, and the external air fluid domain, as shown in the figure. In the combustion chamber fluid domain, kerosene, oxygen and primary nitrogen are injected into the interior of the combustion chamber from the dual airflow atomization nozzle, and the secondary nitrogen is injected tangentially into the interior of the combustion chamber through two small circular holes around the combustion chamber; in the nozzle fluid domain, particles of different sizes and shapes are injected from both sides of the nozzle, and the particle injection speed is controlled by adjusting the pressure of the particle carrier gas; in the external air fluid domain, it is set as a static basin with the same composition and ratio as In the external air fluid domain, the static basin with the same composition and ratio as the air is set to restore the free jet area outside the nozzle to the maximum extent.
数据来源 : 分析测试报告
重点项目名称 : 废旧重型装备损伤检测与再制造形性调控技术
项目所属数据集 : 低温高速火焰喷涂枪设计与建模数据数据集