名称 : 低温高速火焰喷涂2 MPa一次氮气注入的压力场
英文名称 : Pressure field of 2 MPa primary nitrogen injection
材料 : 431
委托单位 : 中国人民解放军军事科学院国防科技创新研究院
实验单位 : 中国人民解放军军事科学院国防科技创新研究院
实验方法 : 无
实验设备 : 无
实验条件 : 无
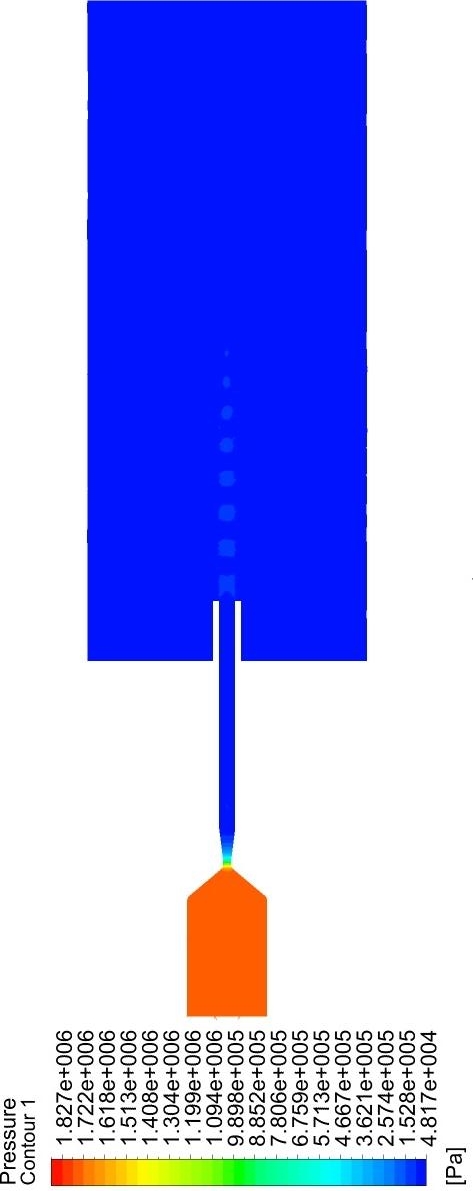
说明 : 以2 MPa一次氮气压力为例对焰流压力进行分析,如图示。从图中可以看出,煤油与氧气在燃烧室内部反应产生大量燃烧气体,此气体不断膨胀,使燃烧室内部形成稳定的气压。随后,气流经过拉瓦尔喷嘴,喷枪内部压力从最大值急剧下降至标准大气压,从云图中可以看到因较大的压力梯度差而产生的激波现象,激波的形成可归因于欠压状态下超音速射流的过度膨胀。
英文说明 : The flame flow pressure is analyzed with 2 MPa primary nitrogen pressure as an example, as shown in the figure. As can be seen from the figure, kerosene reacts with oxygen inside the combustion chamber to produce a large amount of combustion gas, and this gas continuously expands to form a stable air pressure inside the combustion chamber. Subsequently, the gas flow passes through the Laval nozzle, and the pressure inside the gun drops sharply from the maximum to the standard atmospheric pressure, and the surge phenomenon due to the large pressure gradient difference can be seen in the cloud diagram, and the formation of the surge can be attributed to the excessive expansion of the supersonic jet in the underpressure condition.
数据来源 : 分析测试报告
重点项目名称 : 废旧重型装备损伤检测与再制造形性调控技术
项目所属数据集 : 低温高速火焰喷涂枪设计与建模数据数据集